Artificial Intelligence and Marginal Utility
1. What is Marginal Utility?
Marginal utility refers to the satisfaction or benefit gained from consuming one additional unit of a good or service. The marginal utility of labor refers to the additional value a worker contributes to the business or society by working an extra hour or taking on an additional task. This concept directly impacts labor productivity, worker satisfaction, and overall economic performance.
The marginal utility of labor increases or decreases depending on factors such as employee performance, their contributions to work processes, and the value they generate overall. The principle of diminishing marginal utility states that when a worker performs the same task repeatedly, the additional benefit or utility gained from doing so decreases. This principle applies particularly when work processes become monotonous, employees become fatigued, and productivity declines.
2. Solutions and Challenges in Past Industrial Revolutions that Failed to Increase the Marginal Utility of Labor
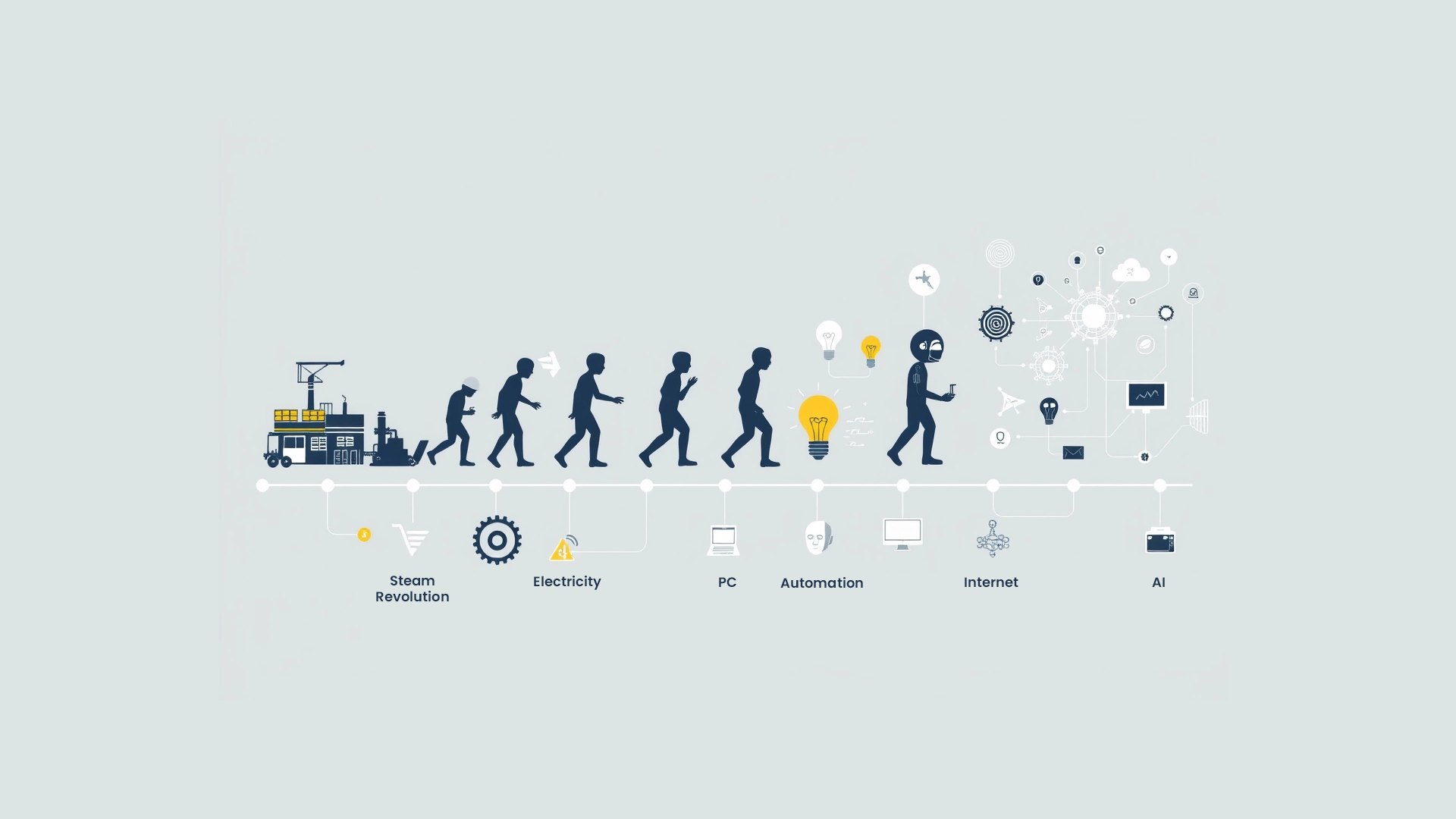
Looking at past industrial revolutions, automation technologies, especially in factories, led to solutions that did not increase the marginal utility of labor, but rather reduced it. For example, during the Second Industrial Revolution, the widespread use of electricity and the introduction of machines into work processes led to many workers losing their jobs or being relegated to less-skilled roles. While this increased production per worker, the marginal utility of workers decreased.
In this period, automation replaced workers with machines, thereby reducing the marginal utility of labor. For instance, a worker performing a manual, skill-based task would determine the marginal utility of that labor, while automation replaced this worker, increasing production but decreasing the value of their work. As a result, the marginal utility of workers decreased, leading to lower job satisfaction and productivity.
However, while mechanization initially reduced the marginal utility of labor, it created a different impact in the long run. Over time, the need for skilled workers who could operate, repair, or optimize machines increased. This allowed workers to be retrained and acquire new skills. Consequently, workers who could use and manage machines saw an increase in their marginal utility, raising the value they brought to the business.
3. Solutions in Past Industrial Revolutions that Increased the Marginal Utility of Labor and Their Benefits
In the Third Industrial Revolution, the widespread use of computer technologies brought solutions with the potential to increase the marginal utility of labor. Computers enabled speed and accuracy in data processing, allowing workers to focus on more complex, value-added tasks. This resulted in workers creating more value and, consequently, increasing their marginal utility.
With the Fourth Industrial Revolution, digitalization and automation technologies further increased the marginal utility of labor. Data analytics and big data technologies enabled workers to take a more active role in decision-making processes, thereby increasing the value they created. These technologies contributed to workers adding more value to work processes, leading to an increase in their marginal utility.
However, the important factor here is the need to structure automation in such a way that it increases the marginal utility of workers while also increasing production volume. For example, workers who collaborate with machines in an integrated manner can become more skilled, which increases their marginal utility and contributes to overall business efficiency.
4. Artificial Intelligence and Solutions That Increase the Marginal Utility of Labor
Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a crucial technology in increasing the marginal utility of labor today. The solutions AI offers allow workers to take more efficient, creative, and strategic roles in work processes, thereby enhancing the marginal utility of labor and increasing the value individuals contribute to the business and economy.
One of the key areas where AI enhances marginal utility is in automating and optimizing work processes. However, this time, automation doesn’t replace workers, but enables them to perform more valuable tasks. For instance, AI-based decision support systems enable workers to make faster and more accurate decisions. These systems, by analyzing big data, allow workers to play a more strategic role in work processes, thereby increasing their marginal utility because they can engage in higher-value work.
Another significant contribution of AI is seen in training and skill development processes. AI can provide personalized training programs tailored to the needs of workers. This enables workers to develop their skills and become more efficient in their tasks. As a result, the marginal utility of workers increases, which positively impacts overall business performance.
5. Example of “Mesai”: AI Increasing the Marginal Utility of Labor in Meetings
Another important area where AI increases the marginal utility of labor is in meeting management. AI-based meeting assistants like “Mesai” are providing revolutionary solutions in this field. Mesai is an AI assistant that records, transcribes, and analyzes meetings, then generates output from these meetings. This technology automates tasks that would traditionally require extensive time and effort from stenographers, assistants, and data entry personnel.
The most crucial aspect of how Mesai increases the marginal utility of labor is by improving meeting efficiency. By automatically generating meeting outputs, participants can focus their time and energy on more strategic tasks. This enhances the marginal utility of labor because workers can create more value with less time spent.
Additionally, Mesai prevents post-meeting disputes. In traditional meeting processes, there may be disagreements between participants regarding decisions or notes taken. This can lead to wasted time and disruptions in work processes. Mesai, by recording and transcribing meetings automatically, ensures that decisions are clearly documented, reducing the likelihood of disputes and ensuring that work processes continue smoothly. This increases the marginal utility of labor because disagreements are resolved quickly, and all parties contribute clearly to decision-making processes.
6. Contributions of Solutions That Create Marginal Utility to the Economy and the Future
Solutions that increase the marginal utility of labor not only benefit individual businesses but also have positive effects on the economy as a whole. These solutions increase productivity, which enhances the competitiveness of businesses and supports economic growth. Technologies like AI optimize work processes and allow workers to use their skills more efficiently, thus increasing marginal utility. This creates higher value for both employers and employees.
Ultimately, solutions that increase the marginal utility of labor are essential for all stakeholders in the economy. These solutions boost productivity, supporting economic growth and sustainable development. In the future, the widespread adoption of these technologies and solutions will contribute to economic stability and sustainable growth. AI, by enhancing the marginal utility of labor, will not only improve individual businesses but also raise the overall well-being of society. In this process, worker job satisfaction will increase as they have the opportunity to perform more skilled, valuable, and creative work. At the same time, businesses will reduce costs with more efficient processes and increase their competitive advantage.
AI solutions maximize the potential of the workforce, increasing the contribution of each individual to the economy. This, in turn, leads to more economic growth, higher living standards, and societal well-being. Therefore, investing in solutions that increase the marginal utility of labor, such as AI technologies, is a critical step in shaping the economy of both today and tomorrow.
In conclusion, AI solutions that enhance the marginal utility of labor ensure the sustainability of economic development and will be a fundamental pillar of future economic success. These solutions not only contribute to economic growth but also promote societal well-being, creating a more just and balanced economic structure. AI-driven solutions that increase the marginal utility of labor will play a key role in building a future that benefits us all.
Other Articles